
Security News
Deno 2.2 Improves Dependency Management and Expands Node.js Compatibility
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.
ansi-escapes
Advanced tools
The ansi-escapes npm package provides a collection of ANSI escape codes for manipulating the terminal. These codes can be used to control cursor movement, erase text, manage scrollback, and more, allowing developers to create interactive command-line applications.
Cursor Movement
Moves the cursor to the specified x and y position (column 5, row 10).
const ansiEscapes = require('ansi-escapes');
console.log(ansiEscapes.cursorTo(5, 10));Erase Lines
Erases the specified number of lines (2 lines in this case) from the current cursor position up.
const ansiEscapes = require('ansi-escapes');
console.log(ansiEscapes.eraseLines(2));Scrolling
Scrolls the terminal viewport up or down one line.
const ansiEscapes = require('ansi-escapes');
console.log(ansiEscapes.scrollUp());
console.log(ansiEscapes.scrollDown());Clearing Screen
Clears the terminal screen and moves the cursor to the upper-left corner.
const ansiEscapes = require('ansi-escapes');
console.log(ansiEscapes.clearScreen);Beep
Triggers the terminal bell, which often makes an audible beep sound.
const ansiEscapes = require('ansi-escapes');
console.log(ansiEscapes.beep);Chalk is a popular package for styling terminal strings with colors and styles but does not include the cursor and screen manipulation features of ansi-escapes.
Blessed is a high-level terminal interface library that includes screen and cursor manipulation, similar to ansi-escapes, but offers a more comprehensive API for building terminal applications.
Cli-cursor allows for showing and hiding the terminal cursor, which is a subset of the functionality provided by ansi-escapes.
Inquirer is a package for creating interactive command-line user interfaces. It uses escape codes under the hood for cursor movement and screen manipulation, similar to ansi-escapes, but provides a higher-level API for building prompts.
ANSI escape codes for manipulating the terminal
npm install ansi-escapes
import ansiEscapes from 'ansi-escapes';
// Moves the cursor two rows up and to the left
process.stdout.write(ansiEscapes.cursorUp(2) + ansiEscapes.cursorLeft);
//=> '\u001B[2A\u001B[1000D'
You can also use it in the browser with Xterm.js:
import ansiEscapes from 'ansi-escapes';
import {Terminal} from 'xterm';
import 'xterm/css/xterm.css';
const terminal = new Terminal({…});
// Moves the cursor two rows up and to the left
terminal.write(ansiEscapes.cursorUp(2) + ansiEscapes.cursorLeft);
//=> '\u001B[2A\u001B[1000D'
Set the absolute position of the cursor. x0 y0 is the top left of the screen.
Set the position of the cursor relative to its current position.
Move cursor up a specific amount of rows. Default is 1.
Move cursor down a specific amount of rows. Default is 1.
Move cursor forward a specific amount of columns. Default is 1.
Move cursor backward a specific amount of columns. Default is 1.
Move cursor to the left side.
Save cursor position.
Restore saved cursor position.
Get cursor position.
Move cursor to the next line.
Move cursor to the previous line.
Hide cursor.
Show cursor.
Erase from the current cursor position up the specified amount of rows.
Erase from the current cursor position to the end of the current line.
Erase from the current cursor position to the start of the current line.
Erase the entire current line.
Erase the screen from the current line down to the bottom of the screen.
Erase the screen from the current line up to the top of the screen.
Erase the screen and move the cursor the top left position.
Scroll display up one line.
Scroll display down one line.
Clear the terminal screen. (Viewport)
Clear the whole terminal, including scrollback buffer. (Not just the visible part of it)
Enter the alternative screen.
Exit the alternative screen, assuming enterAlternativeScreen was called before.
Output a beeping sound.
Create a clickable link.
Supported terminals. Use supports-hyperlinks to detect link support.
Display an image.
Currently only supported on iTerm2 >=3
See term-img for a higher-level module.
Type: Buffer
Buffer of an image. Usually read in with fs.readFile().
Type: object
Type: string | number
The width and height are given as a number followed by a unit, or the word "auto".
N: N character cells.Npx: N pixels.N%: N percent of the session's width or height.auto: The image's inherent size will be used to determine an appropriate dimension.Type: boolean
Default: true
Type: string
Default: process.cwd()
Inform iTerm2 of the current directory to help semantic history and enable Cmd-clicking relative paths.
Creates an escape code to display an "annotation" in iTerm2.
An annotation looks like this when shown:
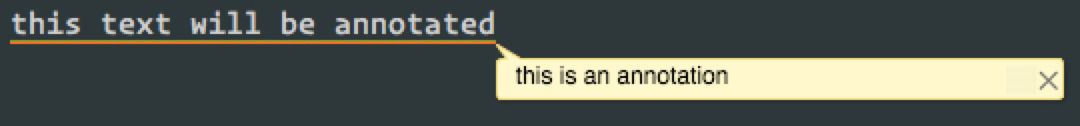
See the iTerm Proprietary Escape Codes documentation for more information.
Type: string
The message to display within the annotation.
The | character is disallowed and will be stripped.
Type: object
Type: number
Default: The remainder of the line
Nonzero number of columns to annotate.
Type: number
Default: Cursor position
Starting X coordinate.
Must be used with y and length.
Type: number
Default: Cursor position
Starting Y coordinate.
Must be used with x and length.
Type: boolean
Default: false
Create a "hidden" annotation.
Annotations created this way can be shown using the "Show Annotations" iTerm command.
FAQs
ANSI escape codes for manipulating the terminal
The npm package ansi-escapes receives a total of 49,954,376 weekly downloads. As such, ansi-escapes popularity was classified as popular.
We found that ansi-escapes demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.2 enhances Node.js compatibility, improves dependency management, adds OpenTelemetry support, and expands linting and task automation for developers.

Security News
React's CRA deprecation announcement sparked community criticism over framework recommendations, leading to quick updates acknowledging build tools like Vite as valid alternatives.

Security News
Ransomware payment rates hit an all-time low in 2024 as law enforcement crackdowns, stronger defenses, and shifting policies make attacks riskier and less profitable.